Can Ldr Str Be Used With Non Registers Assembly
The amount of registers depends on the ARM version. According to the ARM Reference Transmission, there are 30 full general-purpose 32-bit registers, with the exception of ARMv6-K and ARMv7-One thousand based processors. The commencement 16 registers are accessible in user-level style, the boosted registers are available in privileged software execution (with the exception of ARMv6-Grand and ARMv7-M). In this tutorial series nosotros will piece of work with the registers that are accessible in whatever privilege style: r0-15. These 16 registers can be divide into two groups: full general purpose and special purpose registers.

The following tabular array is only a quick glimpse into how the ARM registers could relate to those in Intel processors.
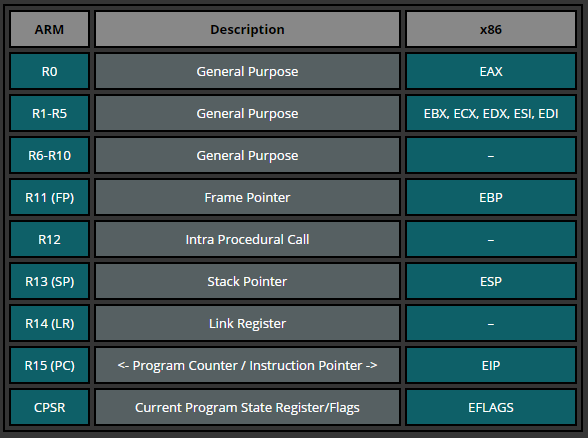
R0-R12: can be used during mutual operations to store temporary values, pointers (locations to memory), etc. R0, for case, can be referred as accumulator during the arithmetic operations or for storing the result of a previously chosen function. R7 becomes useful while working with syscalls as it stores the syscall number and R11 helps united states to proceed track of boundaries on the stack serving as the frame arrow (will exist covered afterwards). Moreover, the function calling convention on ARM specifies that the first four arguments of a office are stored in the registers r0-r3.
R13: SP (Stack Arrow). The Stack Pointer points to the summit of the stack. The stack is an area of memory used for part-specific storage, which is reclaimed when the part returns. The stack pointer is therefore used for allocating infinite on the stack, past subtracting the value (in bytes) we want to allocate from the stack pointer. In other words, if we want to allocate a 32 bit value, we subtract 4 from the stack pointer.
R14: LR (Link Register). When a function telephone call is fabricated, the Link Register gets updated with a memory address referencing the next educational activity where the function was initiated from. Doing this allows the program return to the "parent" function that initiated the "child" role call after the "kid" function is finished.
R15: PC (Program Counter). The Program Counter is automatically incremented past the size of the education executed. This size is always iv bytes in ARM country and 2 bytes in Pollex style. When a co-operative educational activity is beingness executed, the PC holds the destination accost. During execution, PC stores the accost of the electric current instruction plus viii (two ARM instructions) in ARM state, and the current instruction plus iv (ii Thumb instructions) in Thumb(v1) land. This is different from x86 where PC always points to the next instruction to be executed.
Permit's look at how PC behaves in a debugger. We employ the post-obit program to store the accost of pc into r0 and include two random instructions. Let'due south come across what happens.
.section .text .global _start _start: mov r0, pc mov r1, #2 add together r2, r1, r1 bkpt
In GDB we gear up a breakpoint at _start and run it:
gef> br _start Breakpoint 1 at 0x8054 gef> run
Hither is a screenshot of the output we see first:
$r0 0x00000000 $r1 0x00000000 $r2 0x00000000 $r3 0x00000000 $r4 0x00000000 $r5 0x00000000 $r6 0x00000000 $r7 0x00000000 $r8 0x00000000 $r9 0x00000000 $r10 0x00000000 $r11 0x00000000 $r12 0x00000000 $sp 0xbefff7e0 $lr 0x00000000 $pc 0x00008054 $cpsr 0x00000010 0x8054 <_start> mov r0, pc <- $pc 0x8058 <_start+four> mov r0, #2 0x805c <_start+8> add r1, r0, r0 0x8060 <_start+12> bkpt 0x0000 0x8064 andeq r1, r0, r1, asr #10 0x8068 cmnvs r5, r0, lsl #2 0x806c tsteq r0, r2, ror #18 0x8070 andeq r0, r0, r11 0x8074 tsteq r8, r6, lsl #6
We can encounter that PC holds the address (0x8054) of the next teaching (mov r0, pc) that will exist executed. Now allow'south execute the side by side instruction after which R0 should agree the address of PC (0x8054), right?
$r0 0x0000805c $r1 0x00000000 $r2 0x00000000 $r3 0x00000000 $r4 0x00000000 $r5 0x00000000 $r6 0x00000000 $r7 0x00000000 $r8 0x00000000 $r9 0x00000000 $r10 0x00000000 $r11 0x00000000 $r12 0x00000000 $sp 0xbefff7e0 $lr 0x00000000 $pc 0x00008058 $cpsr 0x00000010 0x8058 <_start+4> mov r0, #2 <- $pc 0x805c <_start+eight> add r1, r0, r0 0x8060 <_start+12> bkpt 0x0000 0x8064 andeq r1, r0, r1, asr #10 0x8068 cmnvs r5, r0, lsl #2 0x806c tsteq r0, r2, ror #18 0x8070 andeq r0, r0, r11 0x8074 tsteq r8, r6, lsl #vi 0x8078 adfcssp f0, f0, #4.0
…correct? Incorrect. Look at the address in R0. While we expected R0 to contain the previously read PC value (0x8054) it instead holds the value which is two instructions alee of the PC we previously read (0x805c). From this example you can run across that when nosotros directly read PC it follows the definition that PC points to the next didactics; just when debugging, PC points two instructions ahead of the current PC value (0x8054 + 8 = 0x805C). This is because older ARM processors always fetched two instructions alee of the currently executed instructions. The reason ARM retains this definition is to ensure compatibility with earlier processors.
Can Ldr Str Be Used With Non Registers Assembly,
Source: https://azeria-labs.com/arm-data-types-and-registers-part-2/
Posted by: mckenzieallat1971.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Can Ldr Str Be Used With Non Registers Assembly"
Post a Comment